
Build and Deploy in SaaS-COSS: Insights from Preset and Apache Superset
As a commercial open-source (COSS) company like Preset, we are no strangers to the benefits this model offers. Our alliance with a high-velocity open-source project, Apache Superset, has fostered innovation, cost efficiency, and community support while enhancing our capability to address market demands and user-specific needs.
However, COSS companies face complexities, including release management. While the challenge is neither unique to Preset nor impossible to solve, it requires purposeful management to ensure the continued prosperity of the symbiotic relationship between open-source projects and commercial entities.
If you are coming from a traditional closed-source enterprise background, the first thing you would notice is that the branching strategy for release management is not just a discussion; it is a religion. For example, if you fork the codebase, you can stabilize the releases faster but may run head-first into merge conflicts. On the other hand, if you don't fork it, you may encounter issues with picking up changes that could interfere with non-open-source proprietary features.
The use cases for specific features are extremely wide, as they span across multiple organizations that contribute source code to address their specific needs. Not all of these use cases are explicitly communicated with the community members, introducing the challenge of wide non-enumerable feature permutations that may interfere with each other in unknown or unpredictable ways.
In this blog, we will share how Preset tackles these challenges and how we are evolving our approach and tactics with each release.
Release Management: Overall Process
Preset is committed to the continuous improvement and enhancement of Apache Superset, and our development process plays a vital role in achieving this goal. We consider the community as an integral part of our work, and there is no distinction between changes from our team and contributions from the community. Everything related to Superset is merged into the Apache Superset codebase and made readily available for everyone.
Our development cycle operates on a two-week “sprint” system (refer to Table 1 for definitions). At the end of each sprint, we combine updates from Superset's master branch and Preset's customizations to create a release branch. This branch, known as the "Release Candidate," undergoes rigorous testing (see Figure 1).
Figure 1: Testing process after the “Release Candidate” is passed to the QA team.
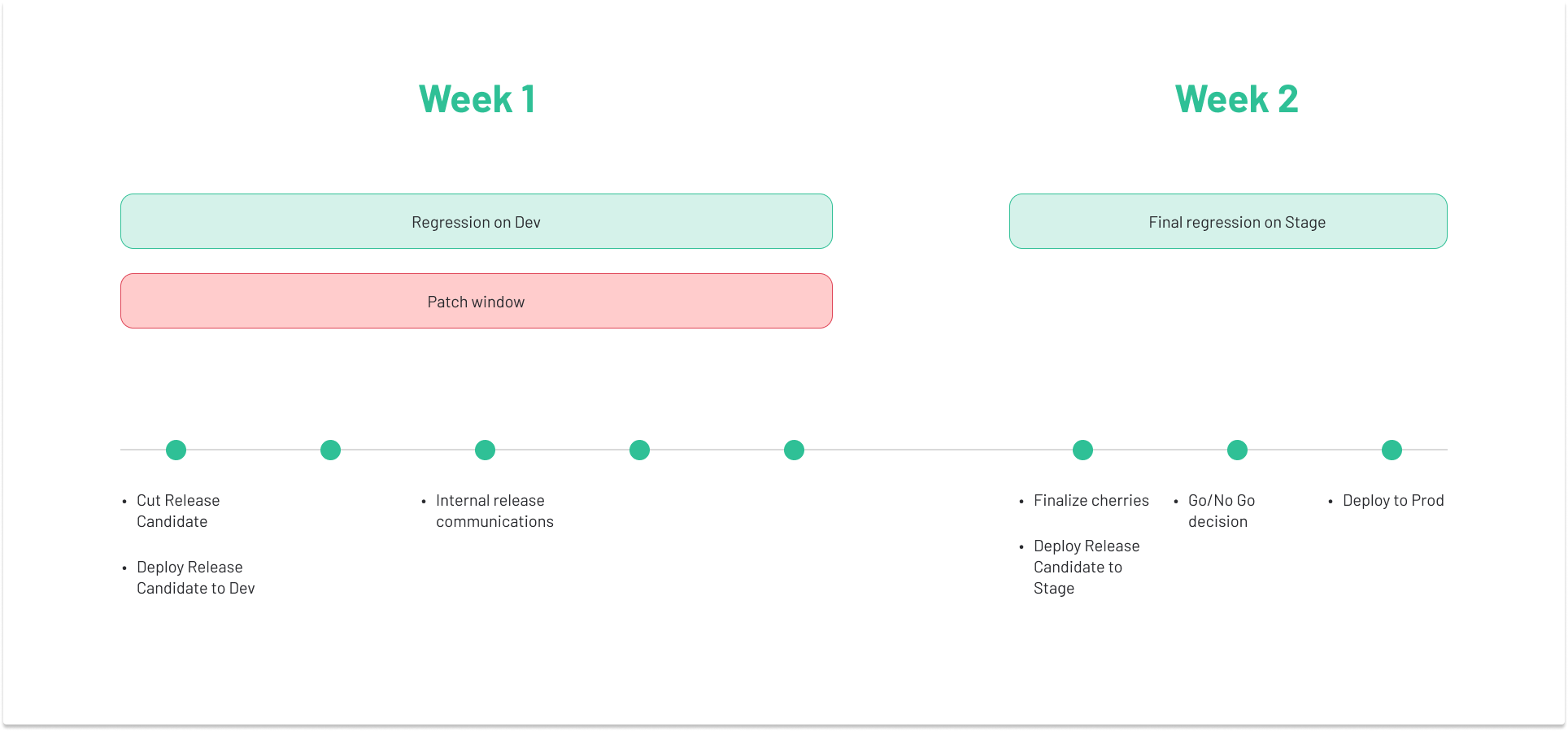
Before handing the Release Candidate to our Quality Assurance (QA) team, we conduct tests to ensure that our customizations have not caused any issues. Once the tests are successfully passed, the QA team takes over and initiates end-to-end automation and manual checks of our primary workflows. This initial testing phase typically lasts three to four days (Week 1).
During the review, the QA team identifies and logs any bugs. These bugs are then carefully examined and prioritized by our Engineering and Product teams to determine their impact on the Release Candidate. Essential bug fixes are incorporated into the upcoming release.
Once all bugs have been addressed, the QA team performs a final round of checks (Week 2). They ensure that not only the fixes work but also that no new issues have been inadvertently introduced. After these checks, we deploy the updates to Preset’s customers and then reset the cycle, ready to start a new sprint.
Table 1: Release management terminology
| Terminology | Definition |
|---|---|
| Sprint | A specific period, in our case, two weeks, during which a set of work is completed and prepared for review. |
| Release candidate | A version of the product that could potentially be released to customers as the final product, provided it passes the final testing phase. |
| Master branch | A primary branch in version control systems like Git, where updates are usually merged. |
| Cherry-pick | A term used in version control systems to describe the action of selecting a subset of changes and applying them to a different branch. |
| End-to-end automation | A method of testing where our QA team checks the entire software from start to finish to ensure it's working as expected. |
Validation and Verification Process
Continuous integration ensures that the changes to the codebase are validated, tested, and verified as soon as possible.
We use the DORA (DevOps Research and Assessment) metrics for release management. DORA metrics refer to a set of key performance indicators (KPIs) used to measure the effectiveness of a software development team's release management practices. These metrics include deployment frequency, lead time for changes, time to restore service, and change failure rate. By tracking these metrics, teams can identify areas for improvement and make data-driven decisions to optimize their release management processes. For a large SaaS platform, the primary metric is the ability to deploy code quickly, as it directly impacts recovery time. We have been able to sustain deployment times of a few minutes for a single workspace and less than 30 minutes for the entire multi-tenant platform.
Apache Superset boasts a vibrant community of users and contributors. This community actively tests Superset releases and assists in managing and resolving bug reports. At Preset, we build upon the testing conducted by the community and take the verification and validation process a step further. We address specific gaps through Preset-specific validation, which includes the following.
- Compatibility Testing: Superset is designed to work with a wide range of operating systems, frameworks, and dependencies. We focus on compatibility testing across platforms and dependency versions used by Preset users to ensure the product functions as intended.
- Customization Testing: Superset allows users to customize and extend its functionality. Preset's QA team tests various customization scenarios utilized by Preset's customers, ensuring that the product remains stable, maintains compatibility with future updates, and handles customizations without introducing regressions or conflicts.
- Functional Testing: Like any non-open source product, we also focus on functional requirements. We ensure that the product behaves as specified in the requirements and meets the intended functionality without any issues or regressions for all new and existing core feature sets.
- Security Testing: As the source code is publicly available, security testing and patching become critical for identifying vulnerabilities and potential exploits and for ensuring data protection. We run a set of comprehensive security testing, including penetration testing, vulnerability scanning, and security audits, to mitigate risks.
- Usability Testing: Since Preset serves teams of all user types from business users to technical users, usability testing becomes crucial. We focus on evaluating the user experience, intuitiveness, and accessibility of the product, ensuring it meets user expectations and is easy to use.
Summary
An open-source project offers flexibility and economic benefits, but effectively managing releases to fully leverage continuous product development can be a challenge for many organizations.
Our dedicated QA team ensures that Preset runs on the latest version of Superset and undergoes thorough validation every two weeks. To learn more about Preset, reach out to our team today!